
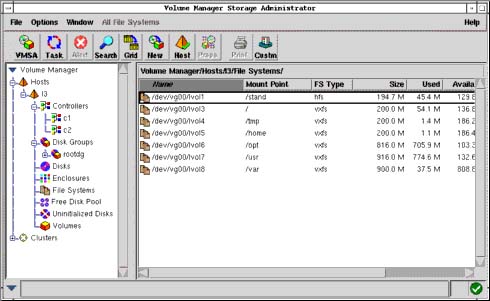
VGs and LVs can be made active as the underlying devices become available through use of the lvmetad daemon.LVM objects can be tagged for administrative convenience.
#Volume manager Offline
This can be useful when migrating whole LVs to or from offline storage. VGs can be split or merged in situ as long as no LVs span the split.Creation of read-only snapshots of logical volumes (LVM1), leveraging a copy on write (CoW) feature, or read/write snapshots (LVM2).Logical volumes (LVs) can be resized online by concatenating extents onto them or truncating extents from them.Volume groups (VGs) can be resized online by absorbing new physical volumes (PVs) or ejecting existing ones.Various elements of the LVM Basic functionality
#Volume manager software
LVM can be considered as a thin software layer on top of the hard disks and partitions, which creates an abstraction of continuity and ease-of-use for managing hard drive replacement, repartitioning and backup. Encrypting multiple physical partitions with one password.

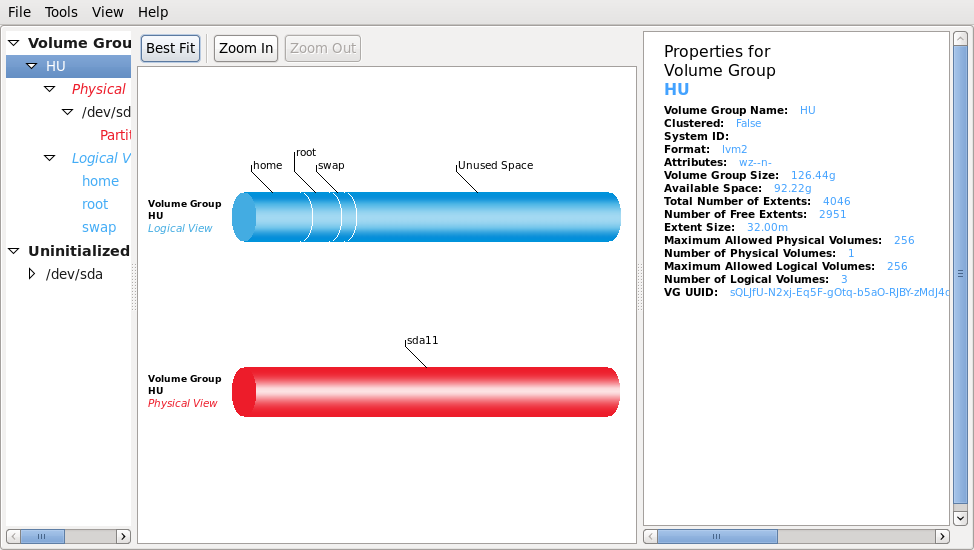
Creating single logical volumes of multiple physical volumes or entire hard disks (somewhat similar to RAID 0, but more similar to JBOD), allowing for dynamic volume resizing.
#Volume manager code
Heinz Mauelshagen wrote the original LVM code in 1998, when he was working at Sistina Software, taking its primary design guidelines from the HP-UX's volume manager. Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to the point of being able to have their root file systems on a logical volume. In Linux, Logical Volume Manager ( LVM) is a device mapper framework that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
